Article de revue (2024)
 Document en libre accès dans PolyPublie et chez l'éditeur officiel Document en libre accès dans PolyPublie et chez l'éditeur officiel |
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Version officielle de l'éditeur Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (13MB) |
|
![[img]](https://publications.polymtl.ca/57372/2.hassmallThumbnailVersion/2024_Antar_Diffusive-thermal_Instabilities_Unstrained_H2O-diluted_Syngas_SUPP1.jpg)
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Image - Matériel supplémentaire Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (637kB) |
|
|
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Vidéo - Matériel supplémentaire Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (1MB) |
|
![[img]](https://publications.polymtl.ca/57372/4.hassmallThumbnailVersion/2024_Antar_Diffusive-thermal_Instabilities_Unstrained_H2O-diluted_Syngas_SUPP3.jpg)
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Image - Matériel supplémentaire Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (460kB) |
|
|
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Vidéo - Matériel supplémentaire Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (535kB) |
|
![[img]](https://publications.polymtl.ca/57372/6.hassmallThumbnailVersion/2024_Antar_Diffusive-thermal_Instabilities_Unstrained_H2O-diluted_Syngas_SUPP5.jpg)
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Image - Matériel supplémentaire Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (781kB) |
|
|
|
Libre accès au plein texte de ce document Vidéo - Matériel supplémentaire Conditions d'utilisation: Creative Commons: Attribution-Utilisation non commerciale-Pas d'oeuvre dérivée (CC BY-NC-ND) Télécharger (930kB) |
Abstract
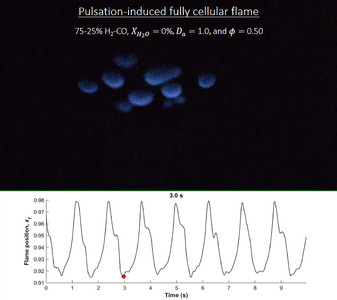
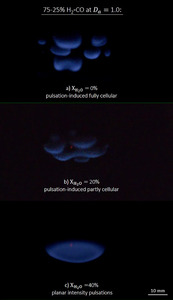
A new version of the unstrained diffusion flame burner that can be operated with gaseous fuels containing high vapor content is introduced. Being a good approximation of the classical chambered diffusion flame solution, the flames generated are nominally unstrained, unlike common research burners where hydrodynamic effects are significant. This permits quantitative comparison with theoretical models that are often based on this simple configuration, and paves the way for fundamental experimental studies with vaporized fuels. In this paper, the capabilities of the new burner design are exploited to study diffusive-thermal instabilities (DTIs) in H2O-diluted H2-CO-CH4-CO2 mixtures. H2O dilution can be significant in biomass-derived syngas mixtures that are not cooled prior to combustion, and that are often burned directly to lower losses as waste heat and pollutant emission in practical combustors. Flammability limits are first presented for a broad range of fuel blends, where the destabilizing effect of H2O dilution is discussed. Instability maps in terms of the Damköhler number are then provided to illustrate the different types of superimposed cellular-pulsating instabilities that onset from the simultaneous presence of H2 with high diffusivity, and CO/CH4 with much lower mobility. The characteristics of these peculiar instabilities are highly dependent on the H2O dilution fraction, which increases both the fuel blend and oxidizer Lewis numbers. The degree of cellularity superimposed in the pulsating multi-fuel flame is reduced at higher water content, as the number of observed cells decreases. The opposite effect is observed on the pulsation frequency, which increases at higher water concentrations.
Mots clés
| Département: | Département de génie mécanique |
|---|---|
| Organismes subventionnaires: | CRSNG/NSERC, Trottier Energy Institute, Fonds de Recherche du Québec Nature et technologies (FRQNT) - Doctoral scholarship |
| Numéro de subvention: | PGSD3-546588-2020, RGPIN-03622–2014, RGPIN-05071–2022 |
| URL de PolyPublie: | https://publications.polymtl.ca/57372/ |
| Titre de la revue: | Combustion and Flame (vol. 261) |
| Maison d'édition: | Elsevier |
| DOI: | 10.1016/j.combustflame.2024.113313 |
| URL officielle: | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2024.113313 |
| Date du dépôt: | 28 févr. 2024 14:05 |
| Dernière modification: | 08 janv. 2026 17:21 |
| Citer en APA 7: | Antar, E., & Robert, É. (2024). Diffusive-thermal instabilities in unstrained H₂O-diluted syngas diffusion flames. Combustion and Flame, 261, 113313 (17 pages). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.combustflame.2024.113313 |
|---|---|
 Statistiques
Statistiques
Total des téléchargements à partir de PolyPublie
Téléchargements par année
Provenance des téléchargements
Dimensions